The economy of Japan is the third largest national economy in the world after the United States and the People's Republic of China and is the world's second largest developed economy.
For three decades from 1960, with US military protection, Japan could ignore military spending and instead budgeting on the economy that it experienced rapid economic growth, which was referred to as the Japanese post-war economic miracle. Japan was able to establish and maintain itself as the world's second largest economy from 1978 until 2010, when it was supplanted by the People's Republic of China. By 1990, income per capita in Japan equalled or surpassed that in most countries in the West.
However, in the second half of the 1980s, rising stock and real estate prices caused the Japanese economy to overheat in what was later to be known as the Japanese asset price bubble caused by the policy of low interest rate by Bank of Japan. The economic bubble came to an abrupt end as the Tokyo Stock Exchange crashed in 1990–92 and real estate prices peaked in 1991. Nonetheless, GDP per capita growth from 2001-2010 has still managed to outpace Europe and the United States.
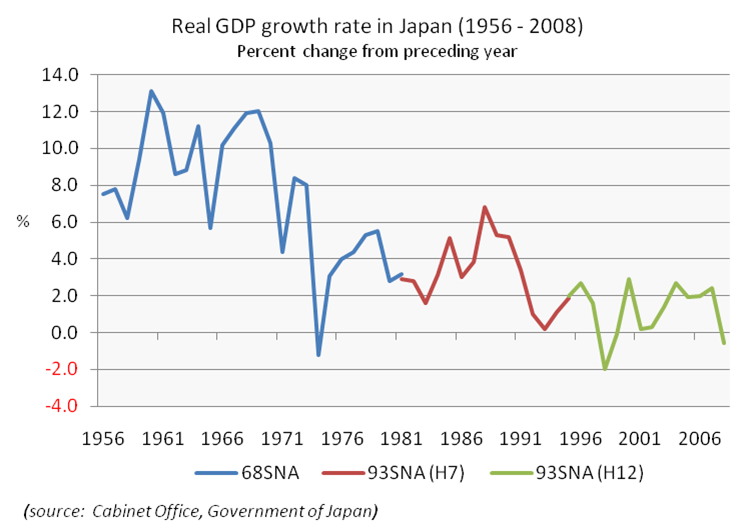
For three decades from 1960, with US military protection, Japan could ignore military spending and instead budgeting on the economy that it experienced rapid economic growth, which was referred to as the Japanese post-war economic miracle. Japan was able to establish and maintain itself as the world's second largest economy from 1978 until 2010, when it was supplanted by the People's Republic of China. By 1990, income per capita in Japan equalled or surpassed that in most countries in the West.
However, in the second half of the 1980s, rising stock and real estate prices caused the Japanese economy to overheat in what was later to be known as the Japanese asset price bubble caused by the policy of low interest rate by Bank of Japan. The economic bubble came to an abrupt end as the Tokyo Stock Exchange crashed in 1990–92 and real estate prices peaked in 1991. Nonetheless, GDP per capita growth from 2001-2010 has still managed to outpace Europe and the United States.

Manufacturing, construction, real estate, services, and communication are Japan's major industries today. Additionally, key industries in Japan's economy are mining, nonferrous metals,
petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, bioindustry, shipbuilding, aerospace, textiles,
and processed foods. Agriculture makes up only about two percent of the GNP. Most important agricultural product is rice. Resources of raw materials are very limited and the mining industry is rather small.
Exports: Japan's main export goods are cars, electronic devices and
computers. Most important trade partners are China and the USA, followed by
South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Thailand and Germany.

没有评论:
发表评论